-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
farm netting
The Importance of Farm Netting in Agriculture
Agriculture has been an essential part of human society for thousands of years, providing food, fiber, and other resources necessary for survival. As techniques and technology have evolved, so have the methods used to protect crops and livestock from various threats. One such method gaining traction among farmers is the use of farm netting. This article explores the importance of farm netting, its various applications, and the benefits it brings to modern agriculture.
Farm netting refers to the use of protective mesh materials that are strategically placed around crops, orchards, and livestock properties to safeguard against a variety of threats, including pests, birds, and harsh weather conditions. With the ever-increasing challenges posed by climate change and an increasing demand for food production, farmers are turning to innovative solutions to enhance their productivity and efficiency. Farm netting is one such solution that offers a range of benefits.
One of the primary advantages of farm netting is its ability to protect crops from birds and insects. Many farmers lose significant portions of their harvests due to avian and insect infestations. By implementing netting, growers can create a physical barrier that deters these animals from accessing their crops. This protection helps to improve overall yield and quality, allowing farmers to meet market demands more effectively.
In addition to protecting against pests, farm netting can also serve as a safeguard against adverse weather conditions. Unpredictable weather patterns, such as heavy rains, hail, and strong winds, can devastate crops in a matter of hours. By using netting, farmers can shield their crops from these elements, reducing the risk of physical damage. The netting can also help maintain a more stable microclimate for plants, providing some insulation during temperature fluctuations.
farm netting
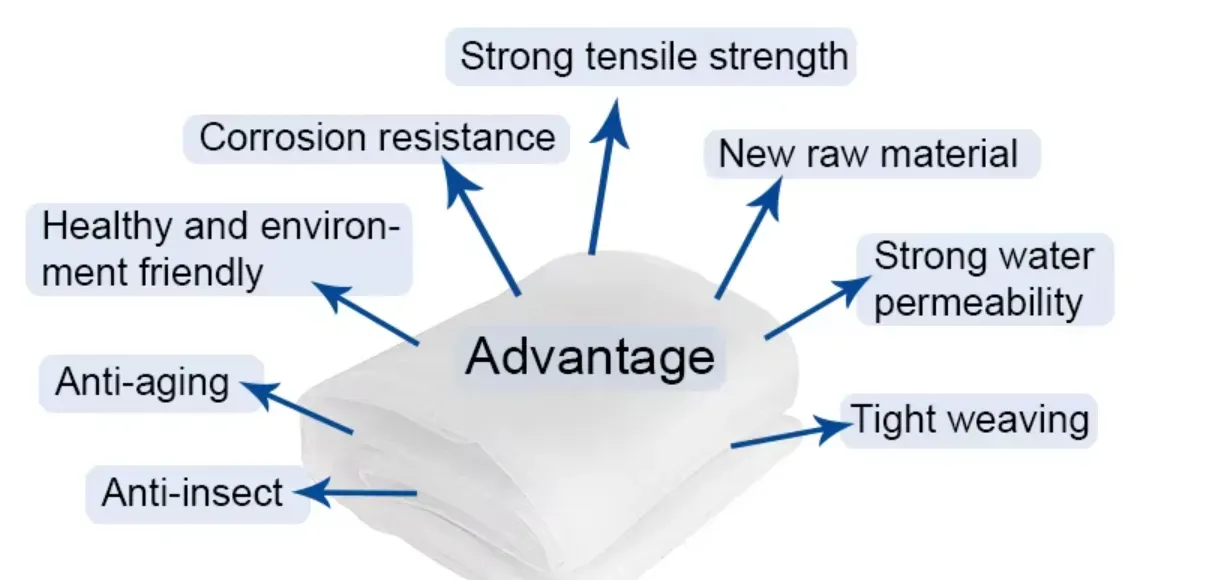
Furthermore, farm netting is an environmentally friendly solution for pest management
. Unlike chemical pesticides, which can have harmful repercussions on the environment and human health, netting offers a non-toxic alternative. By minimizing the use of chemicals, farmers can create a more sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practice. Additionally, this approach aligns with the growing consumer demand for organic and sustainably-produced food.The implementation of farm netting can also lead to cost savings for farmers in the long run. While the initial investment in netting materials may seem significant, the reduction in losses from pests and weather damage can outweigh the costs. Furthermore, as the yield and quality of crops improve, farmers may find themselves enjoying higher profits due to better market prices for their products.
In the context of livestock management, farm netting can be equally beneficial. For instance, netting can be used to create designated areas for free-range poultry or protect feed supplies from animals like deer or coyotes. This not only enhances the well-being of livestock by allowing them to roam freely in a safer environment but also mitigates losses associated with predator attacks.
Moreover, farm netting can help foster biodiversity in agricultural systems. By protecting certain crops from harmful species while allowing beneficial insects to thrive, farmers can promote a more balanced ecosystem on their farms. This biodiversity can lead to healthier soil, improved pollination rates, and an overall increase in farm resilience.
In conclusion, farm netting is an essential tool for modern agriculture, offering a myriad of benefits that contribute to enhancing productivity, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. As farmers face mounting pressures from climate change and ever-growing consumer demands, adopting innovative practices like farm netting will become increasingly crucial. By safeguarding crops and livestock, reducing reliance on chemical pest control, and promoting biodiversity, farm netting stands as a valuable strategy in the pursuit of sustainable farming. The future of agriculture may very well depend on how effectively farmers can integrate such techniques into their operations, ensuring that we meet the nutritional needs of a growing global population while preserving our natural resources for generations to come.
-
Shipping Plastic Bags for Every NeedNewsJul.24,2025
-
Safety Netting: Your Shield in ConstructionNewsJul.24,2025
-
Plastic Mesh Netting for Everyday UseNewsJul.24,2025
-
Nylon Netting for Every UseNewsJul.24,2025
-
Mesh Breeder Box for Fish TanksNewsJul.24,2025
-
Expanded Steel Mesh Offers Durable VersatilityNewsJul.24,2025











